This document will show you how you can add OPC-UA connectivity to RoboDK. An OPC UA connection allows you to interact with PLCs and other devices that support this protocol. You should enable the OPC-UA add-in in RoboDK to add OPC UA server and client features to your projects.
RoboDK includes an OPC-UA add-in that allows you to add OPC UA compatibility to your RoboDK projects.
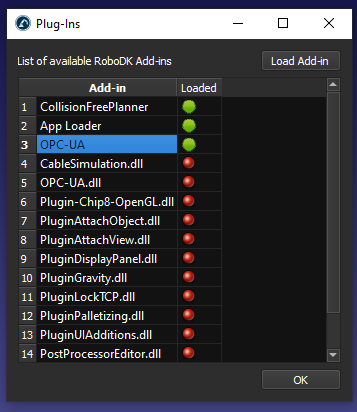
By default, RoboDK has the OPC-UA add-in disabled. Once enabled, the add-in should be displayed every time you start RoboDK.
You can enable the OPC UA add-in by following these steps:
1.Select Tools-Add-ins.
2.Double click on OPC-UA.
You should see an additional toolbar with the OPC-UA features.
//www.sinclairbody.com/addin/com.robodk.plugin.opc-ua.

You should see the OPC-UA button in the Toolbar and also the OPC-UA entry in the menu.
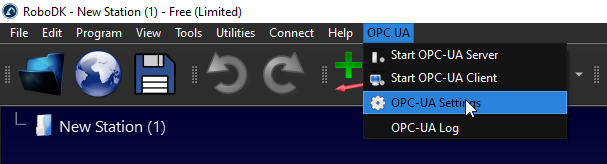
In this example you’ll learn how to enable the OPC UA addin and convert RoboDK into an OPC UA server. We’ll browse some settings by using UaExpert software and Beckhoff TwinCAT3 TF6100.
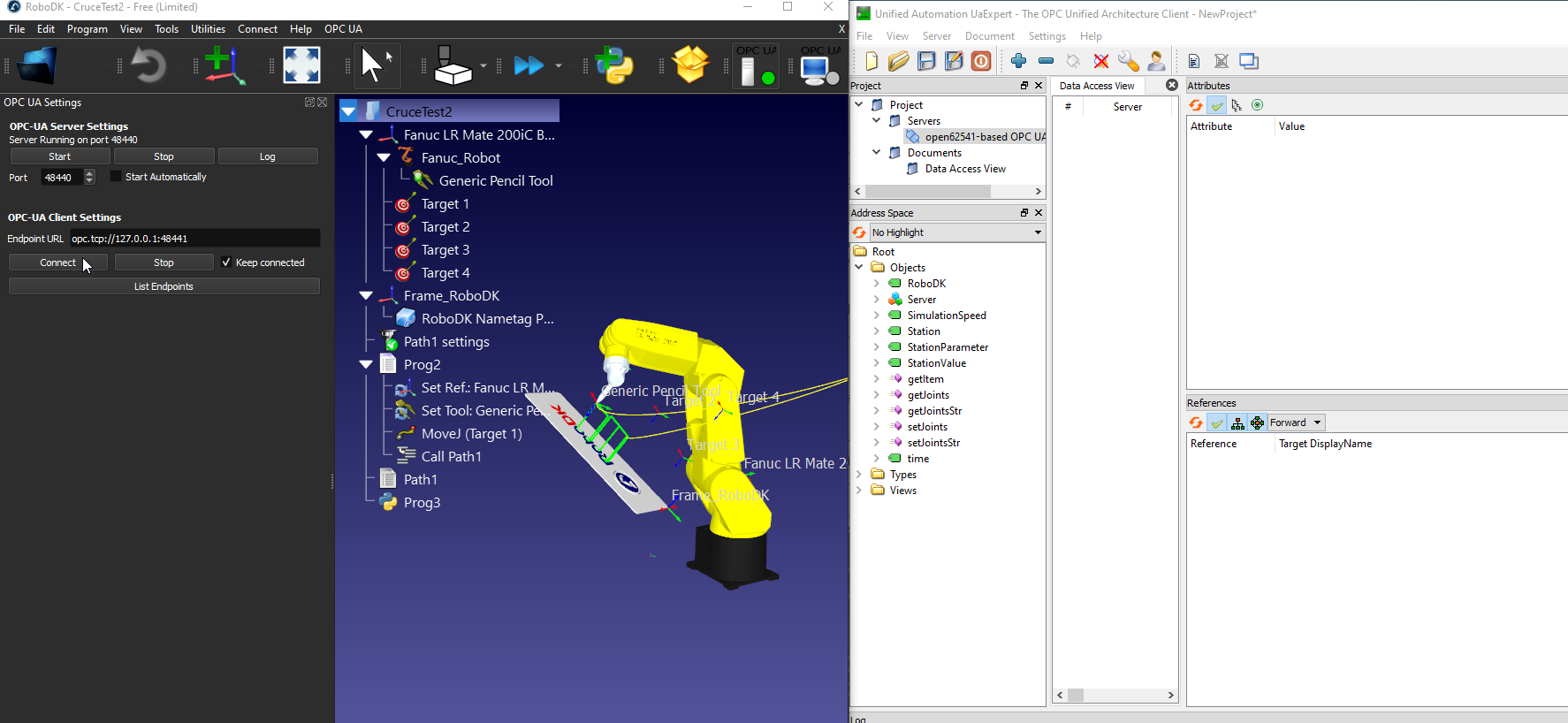
The OPC UA add-in allows you to configure some settings such as the server port. You can also choose to activate the server, deactivate it or automatically start with RoboDK.
With the OPC UA add-in enabled, selectOPC UA-OPC-UA Settingsto configure your OPC UA settings.
OPC UA Settings Screen is shown on the Left side as shown in the following image.
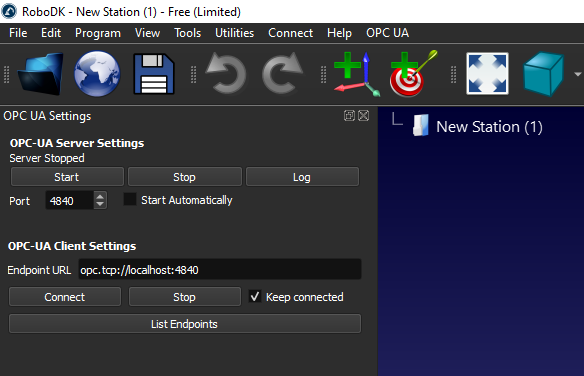
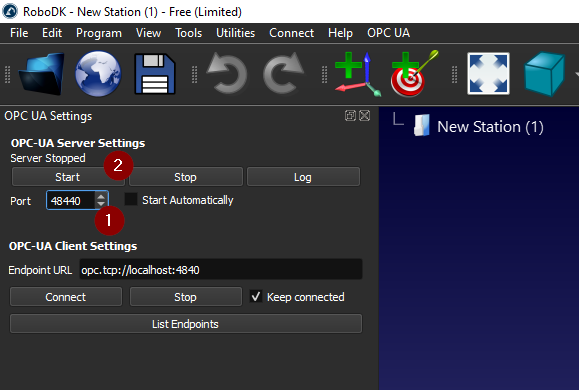
If you see a message such as “RoboDK’s OPC UA server running on port 4840” it means the OPC UA server in RoboDK started.
You can test the OPC UA connectivity with any RoboDK station that has one or more robots.
You can use UaExpert software to test the connectivity with the RoboDK OPC UA Server.
You can download the free version of the UaExpert software from the Unified Automation website:https://www.unified-automation.com/downloads/opc-ua-clients.html.
Launch the UaExpert and Click the “+” Button to Add the RoboDK OPC UA Server.
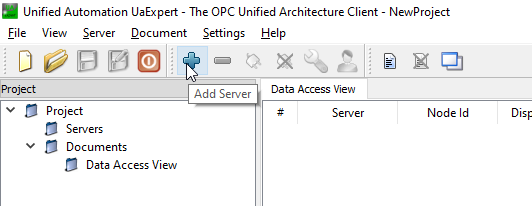
Expand the Custom Discovery and select the
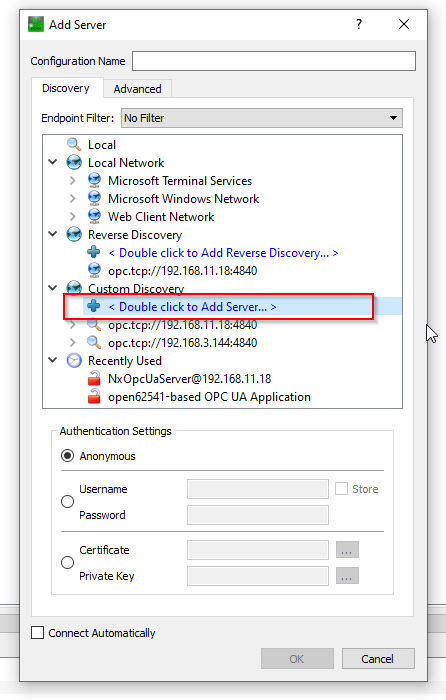
Enter the URL of the OPC UA server, opc.tcp://127.0.0.1:48440 which you configured in the previous step.
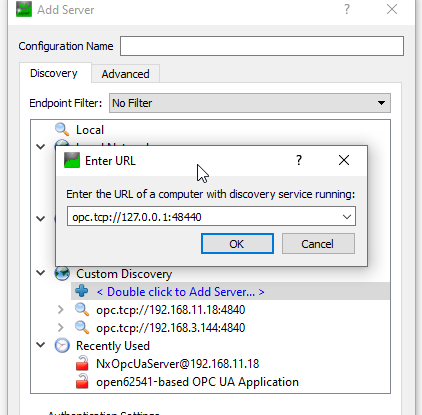
Connect the OPC UA Server with “None” Security.
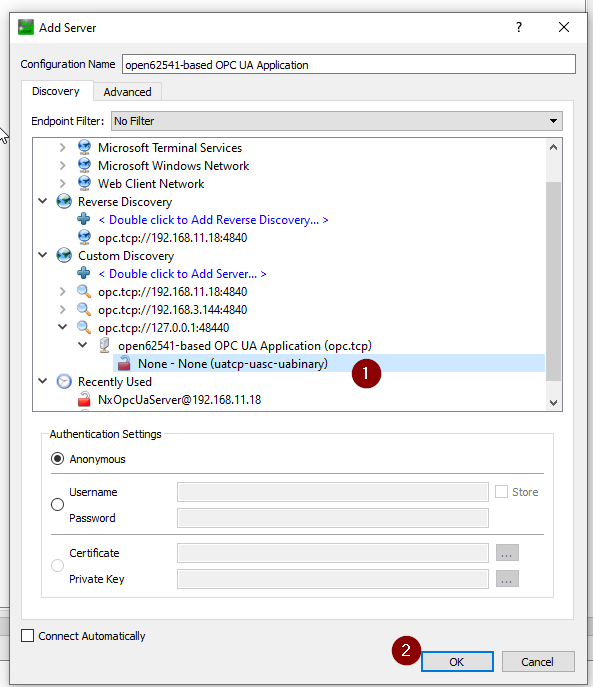
Server is configured.
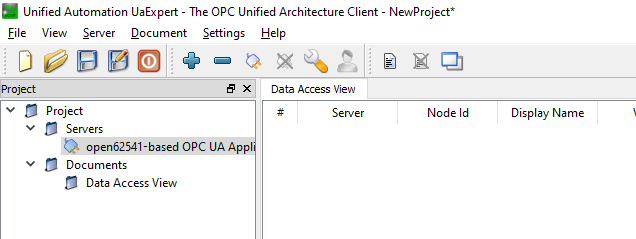
Now you can connect to the RoboDK OPC UA Server from UaExpert.
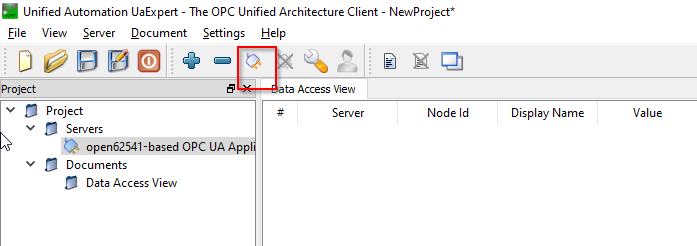
You can see the Nodes and Methods when the connection is established.
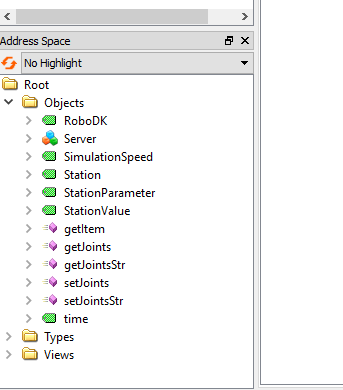
There are some nodes inside the RoboDK OPC UA server to let you exchange some basic information about your station.
RoboDK node is a Node that provides the Actual Version of your RoboDK Software.
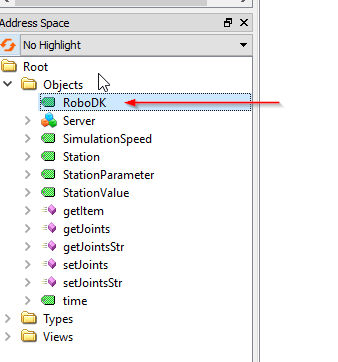
The version RoboDK 64 Bit v5.5.3.23031 was used in this example.
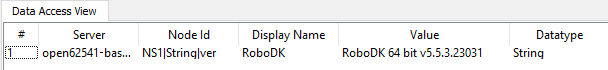
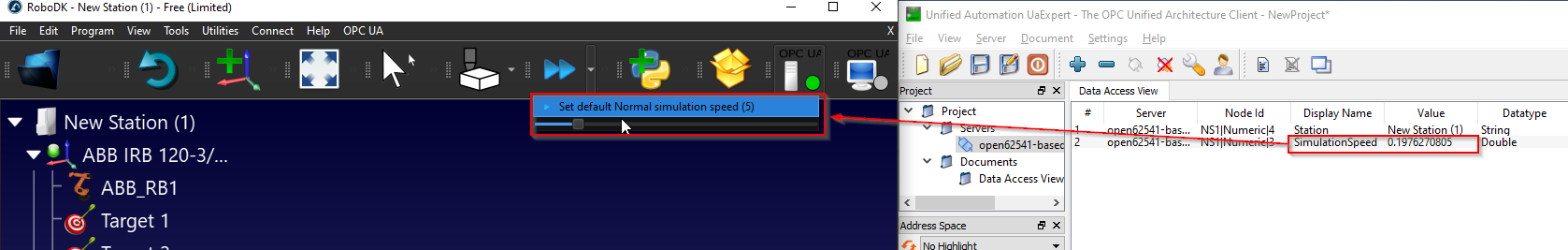
Simulation Speed is a node that shows the actual Simulation Speed and allows the user to overwrite the current Simulation Speed.
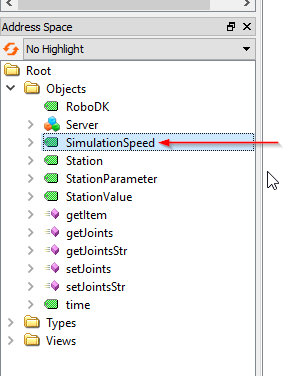
The node value is referenced to the Slide bar of simulation speed.
The current Simulation can be read from this node and can overwrite the simulation speed.
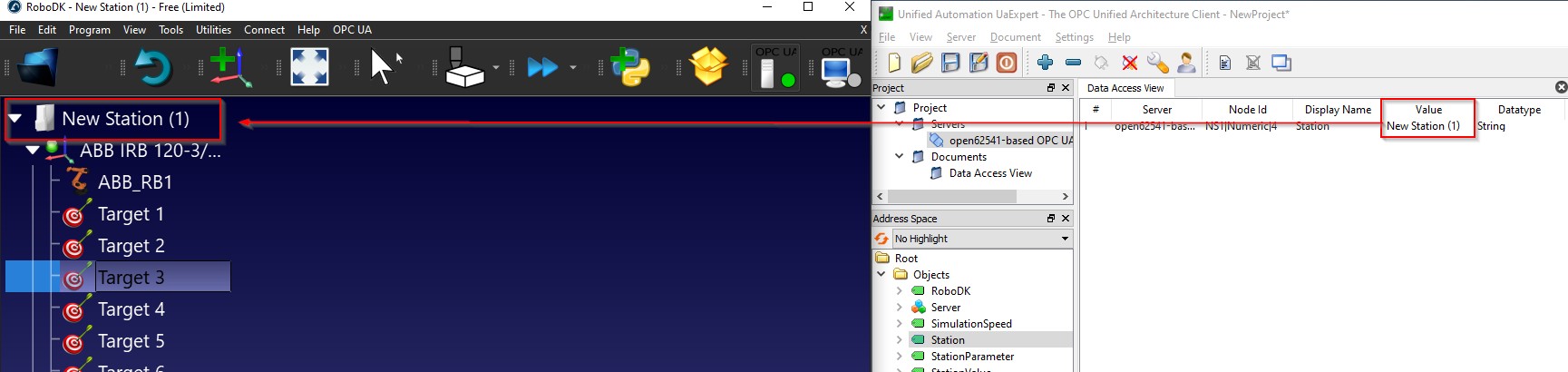
Station Node is a node that allows the user to get the current name of the Station in RoboDK.
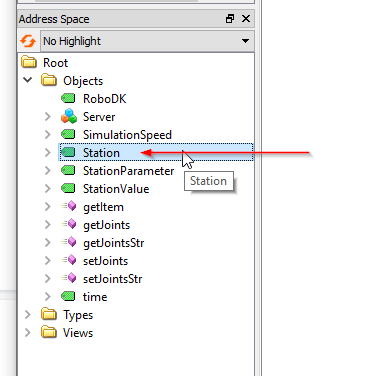
As you see below, the Station node is referenced to your “Station Name” in RoboDK.
Station Parameter and Station Value are a pair set Node that allows the user to get or set any parameters inside your Station. The RoboDK OPC UA Server will continuously monitor the actual value of “StationParameter” and return the Value of that “StationParameter”, from the Station Value Node.
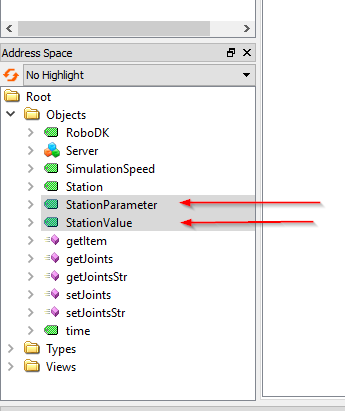
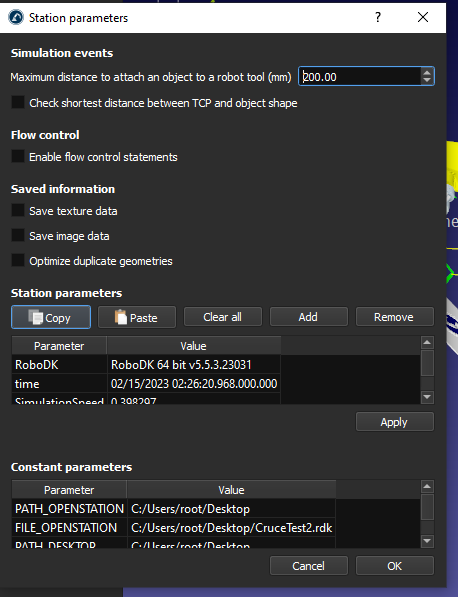
You can view your Station parameters by Right Click your RoboDK Station>Station parameters.
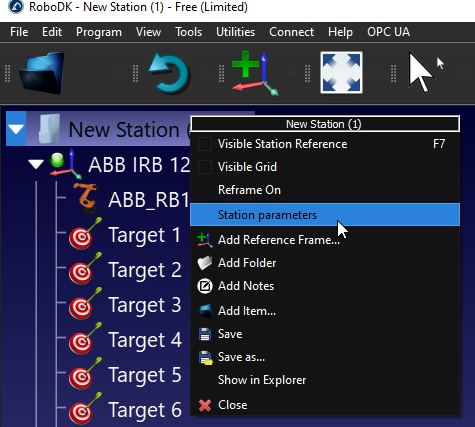
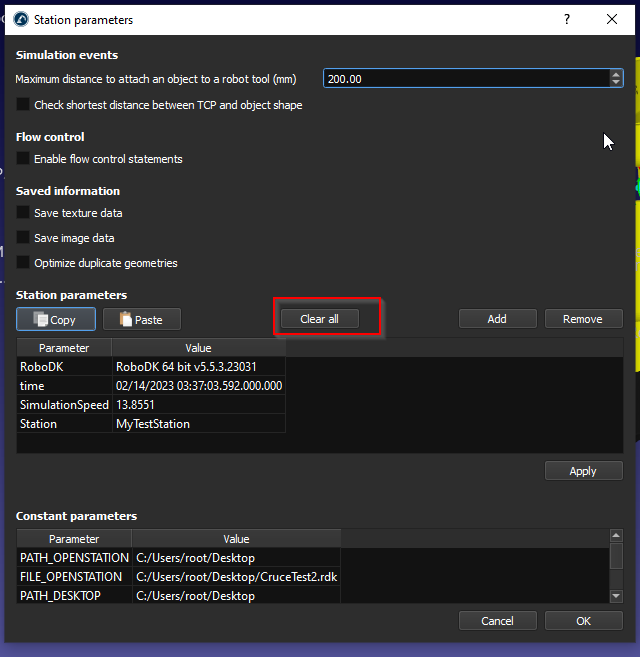
In the Constant parameters field, you can see the default station parameters and their value.
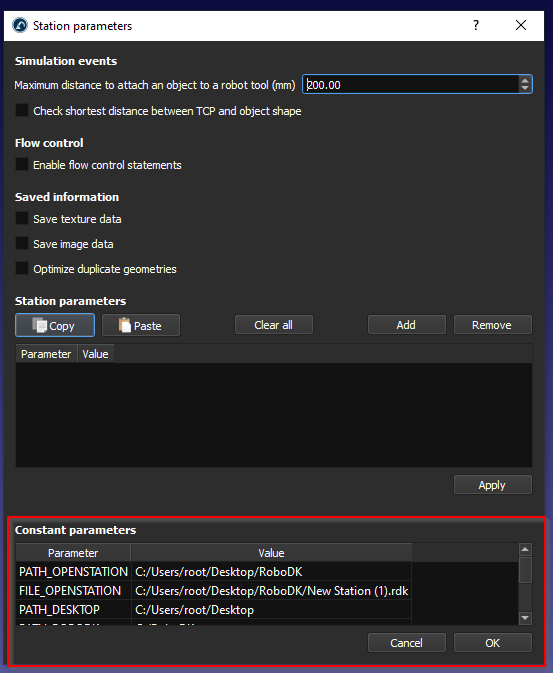
Station parameter is referenced to the “Parameter” field and Station Value is referenced to the “Value” field.
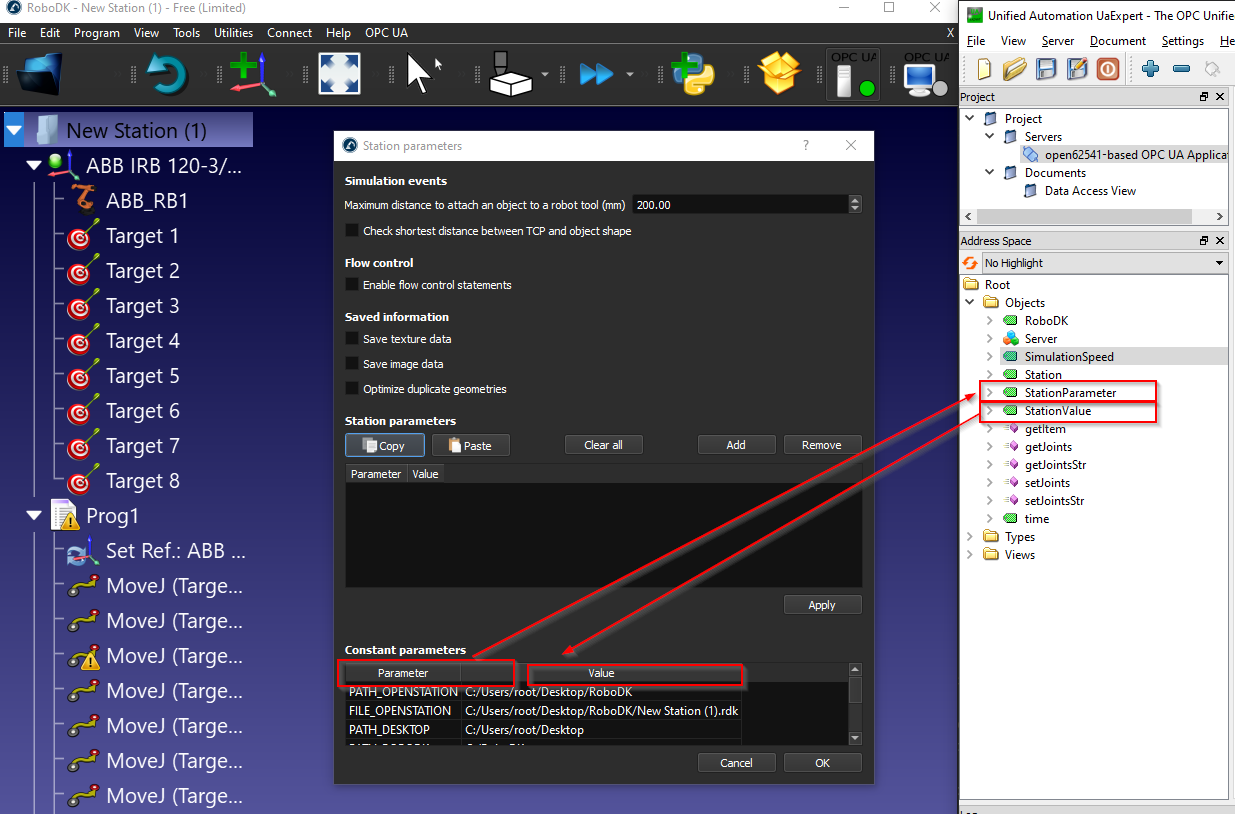
And we can create our own Parameters by clicking the “Add” Button.
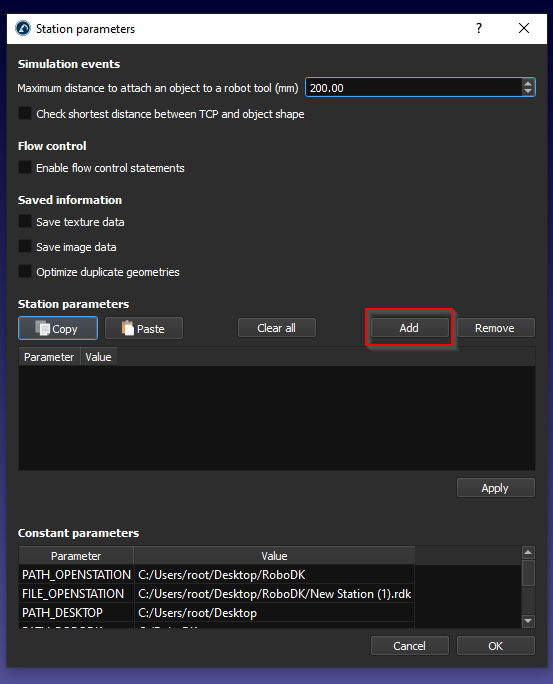
A new Station parameter is added.
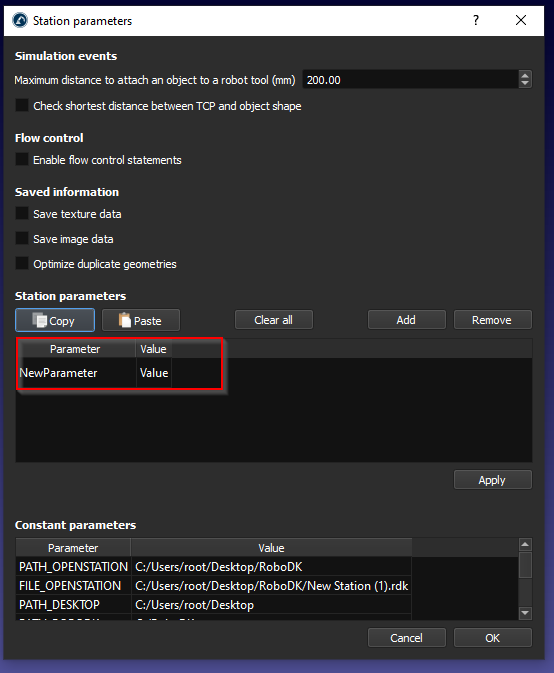
Enter your Parameter name and the Parameter Value, then press Apply to save it.
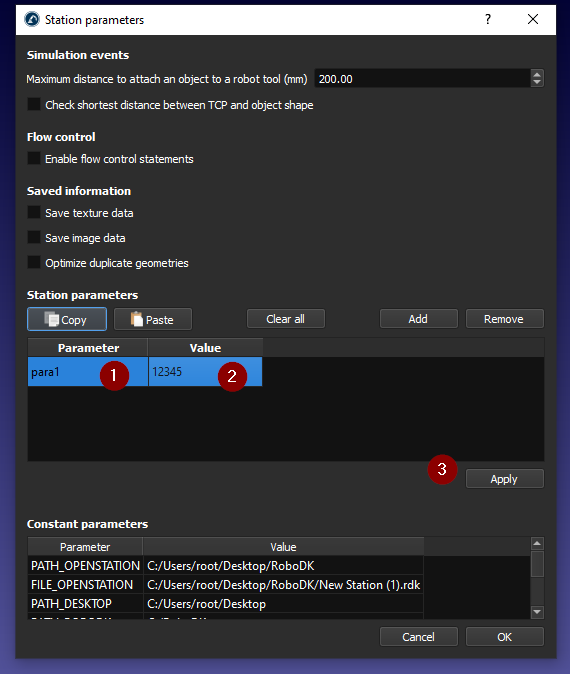
You can get your own station parameter as well.
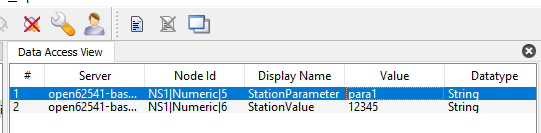
The node time is a node that allows you to get the current time of the RoboDK Station.
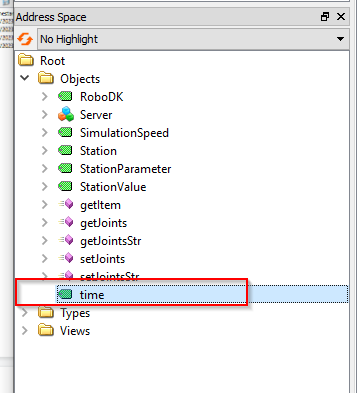
A value with DataTime format is returned.
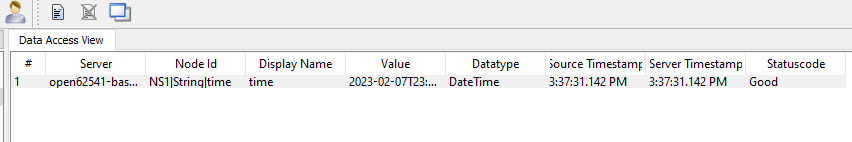
And this Node is updated continually.

RoboDK OPC UA Server is also provided with some methods to allow the user to access the RoboDK station ‘s Data dynamically.
We can just right click the Method>Call to execute the method.
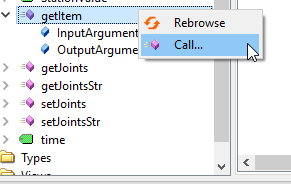
getItem is a Method that allows the user to get the pointer of your Item.
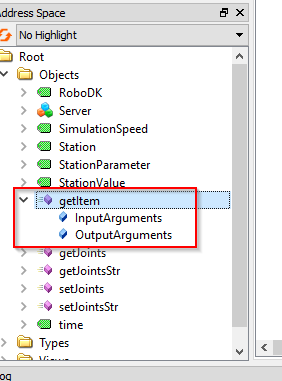
For the InputArguments, Device Name is required, you can image the Device Name is your Station Name,Robot Name..etc.. And Item ID is the OutputArguments that return the Pointer of that Device.
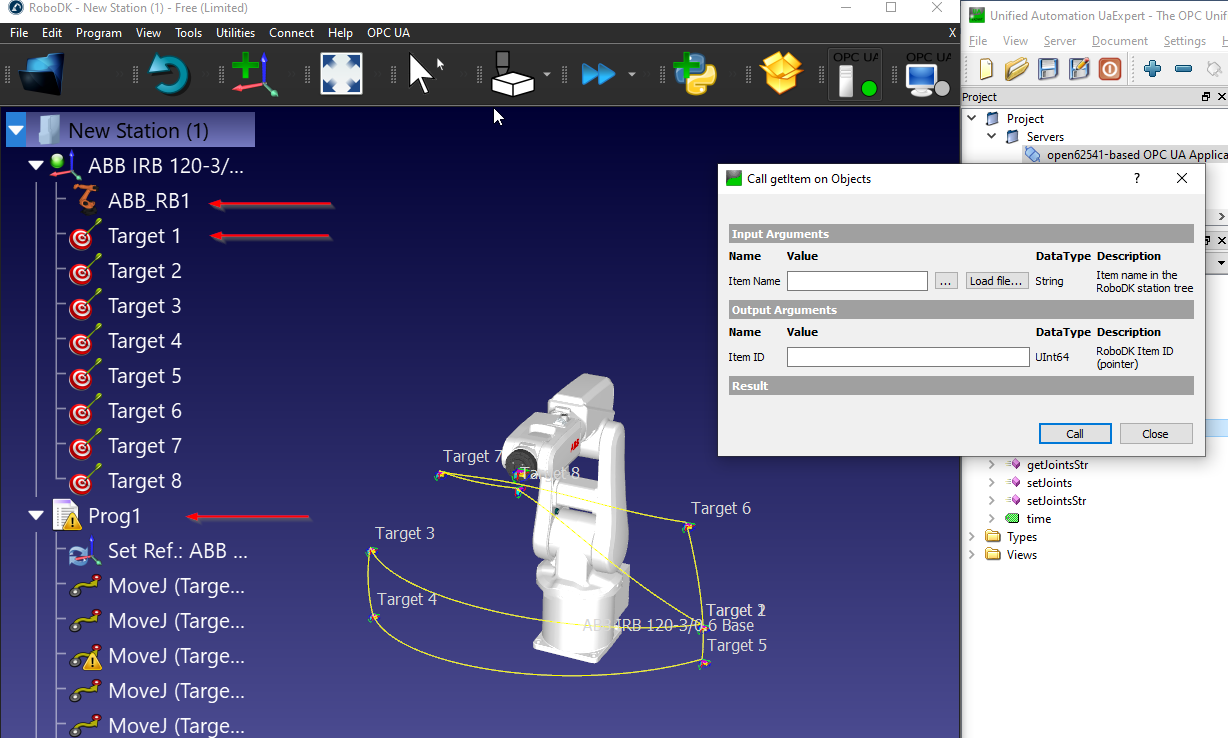
In this Example, I received the Item ID (Pointer) of my ABB Robot that is named as “ABB_RB1”.
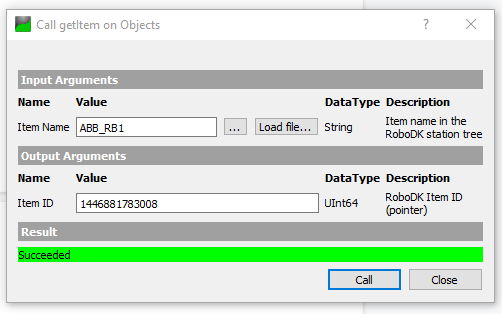
0 is returned if the Item Name is invalid or does not exist inside your station.
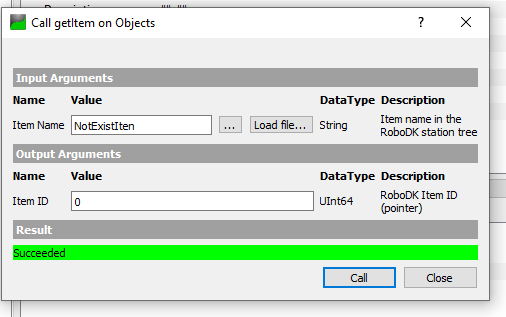
getJonits is a method that allows the user to get the joint value of the robot from the station, based on the Item ID.
The Item ID is the pointer value of your Item, and you can get it from getItem() Method.
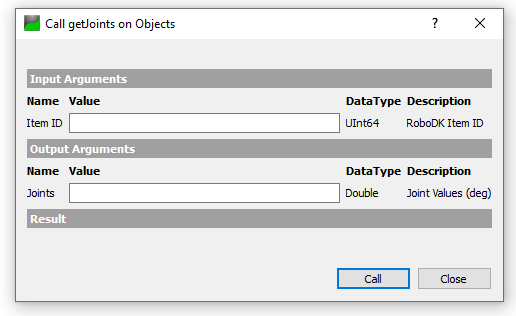
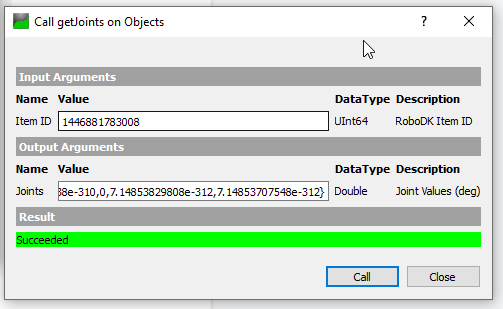
We will get the Item ID with this “ABB_RB1” Item name, and a UInt64 value is returned.

Joints value is returned while passing the Item ID in the method that we got in the previous.
getJointsStr is a method that allows the user to get the Joints value based on a String Value.
We can pass the Robot name (String) in this method.
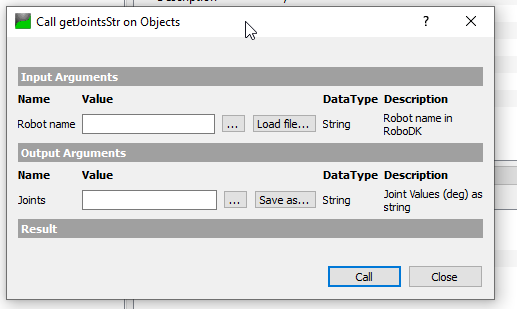
In My Station, ABB_RB1 is my robot’s name.
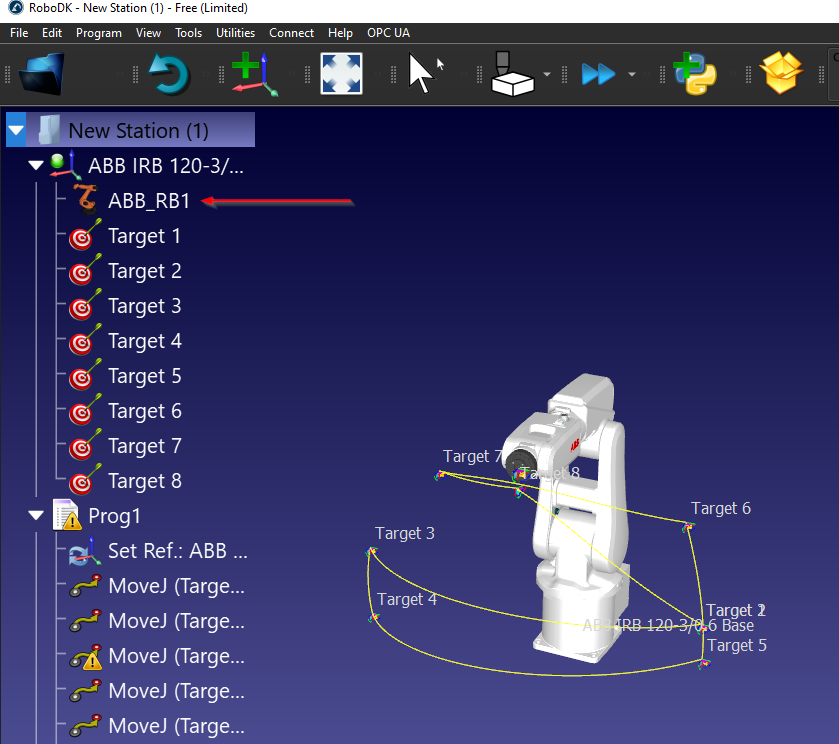
We can just pass “ABB_RB1” in the Robot name parameter and call the method - The joint value in String format is returned.
setJointsStr is a method that allows the user to set the Joints value of the Robot, based on a String Value.
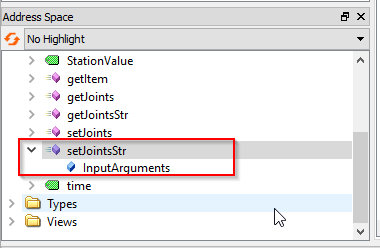
In the Robot name, ABB_RB1 is passed, and we can just pass a string with the joint value in the Joints parameter.
例如:-0.000000,0.000000,-0.000000,-0.000000,-0.0,-0.000000
现在我们可以插入the OPC UA Client by I/O>Devices>Add New Item.
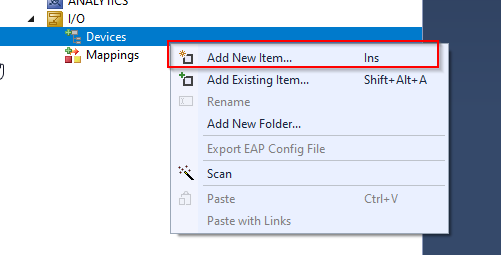
Select Virtual OPC UA Device from OPC >OK.
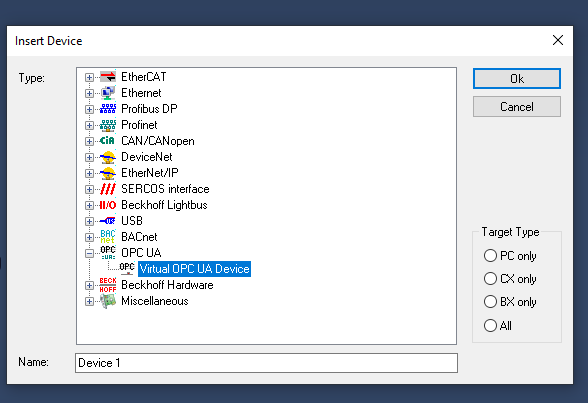
OPC UA Virtual is inserted.
We need to add an OPC UA Client to access the RoboDK OPC UA Server.
Select Device 1 >Right Click >Add New Item.
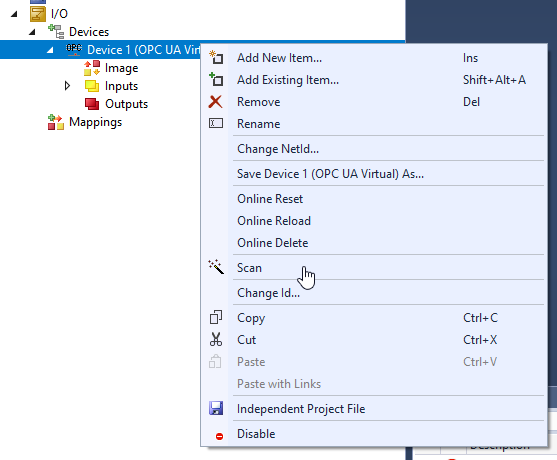
Select “OPC UA Client(Module)” and Ok.
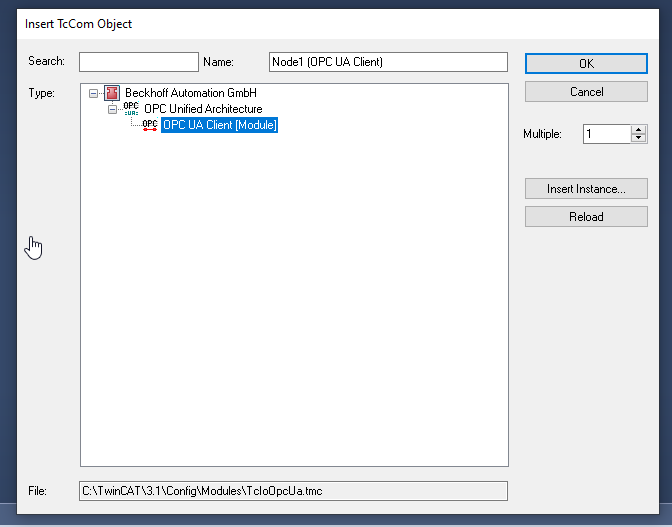
OPC UA Client is inserted.
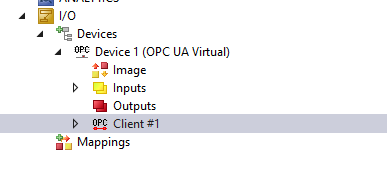
Open the OPC UA Client >Go to Settings Tab>click the “Select Endpoint” to configure the OPC UA Server endpoint that you would like to access.
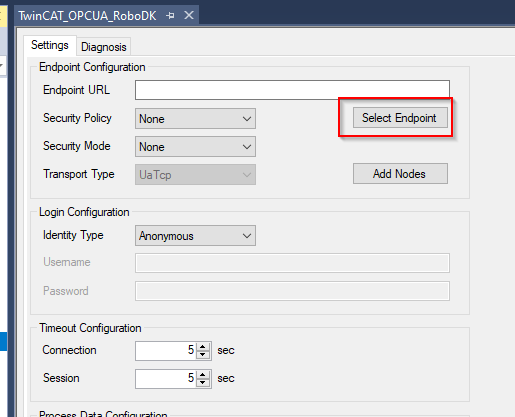
Enter the RoboDK OPC UA server URL and Update it.
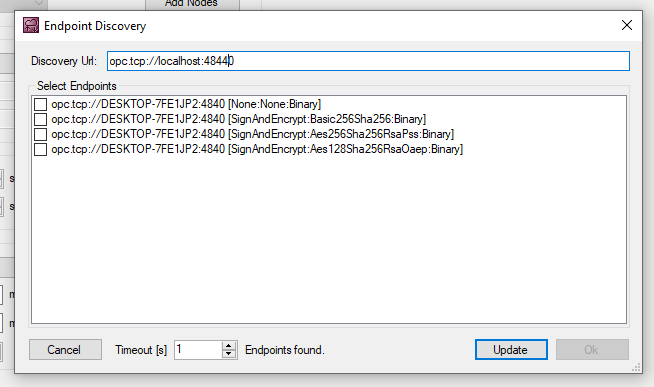
Press “Add Nodes” to browse the node that is inside the OPC UA Server.
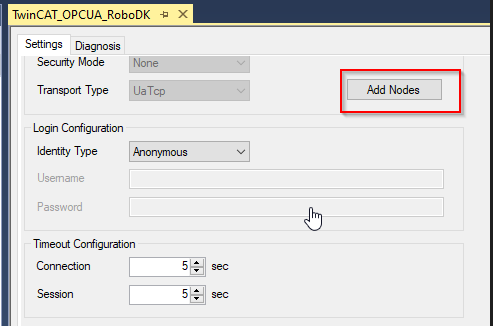
If the connection between TwinCAT and OPC UA Server is established, you can Browse the details of OPC UA server.
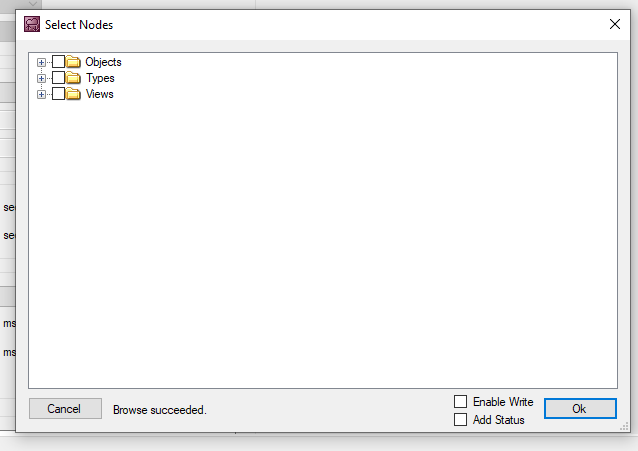
Select all Methods and Ok.
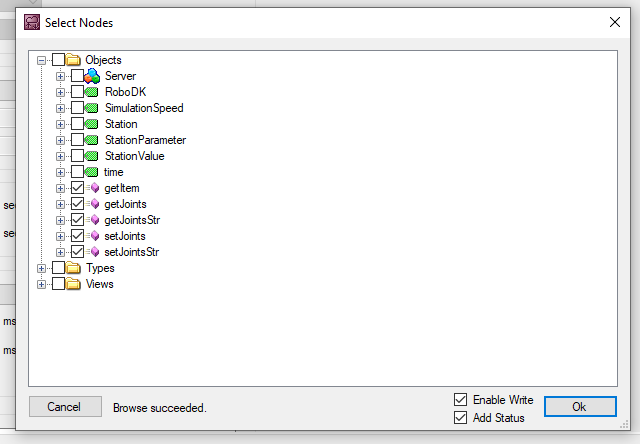
Methods are inserted in your Configuration.
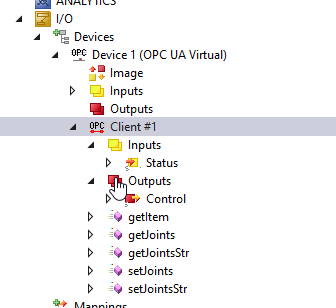
Configure your Name Prefix in this field.
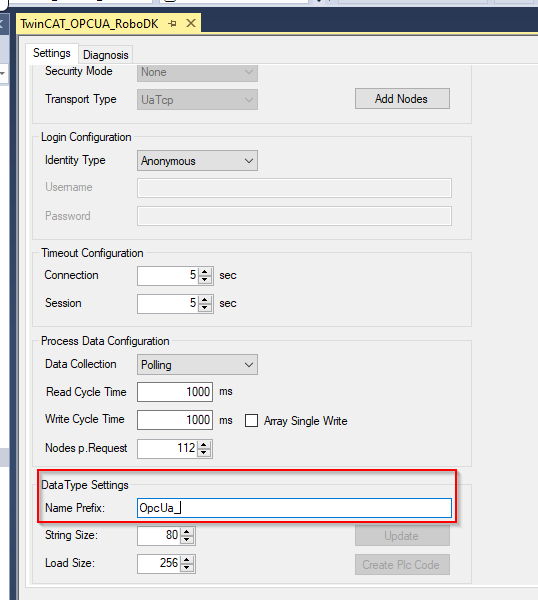
Press “Create Plc Code” to create the PLC Code from TwinCAT.
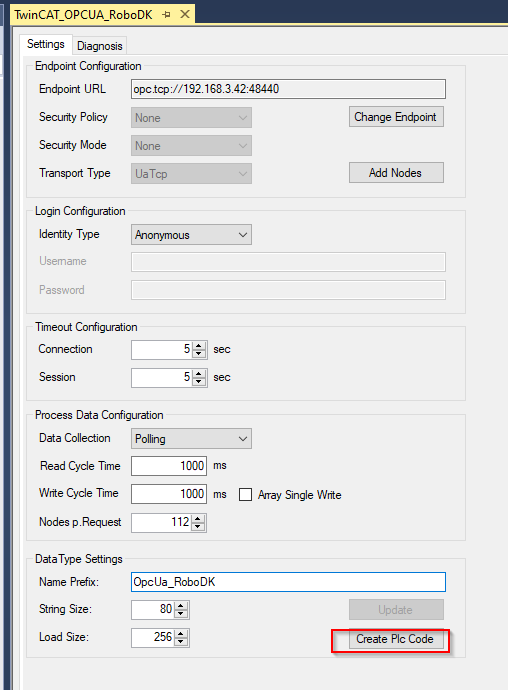
An OpcUaClient folder is created in your project, and all RoboDK Method are created in IEC61131-3 Function Block format.
This section shows a sample program of a Beckhoff TwinCAT PLC that communicates with RoboDK OPC UA server.
PROGRAM MAIN
VAR
bConnected :BOOL;
StationPointer :DINT;
iStep :INT;
bStart :BOOL;;
i :INT;
TON :TON;
bReset :BOOL;
bWrite :BOOL;
TON2 :TON;
bShow :BOOL:=TRUE;
bVis :BOOL:=True;
END_VAR
VAR
Robot_name :STRING(80):='ABB_RB1';
Item_ID :ULINT;
arrJoints :ARRAY[0..11]OF LREAL;
strJoints :STRING(80):='';
arrJointsFromStr:ARRAY[1..11]OF LREAL;
sSeparator :STRING(1) := ',';
arrJointsCommand:ARRAY[1..11]OF LREAL;
strJointsCommand:STRING(80);
END_VAR
VAR CONSTANT
cStepWaitCmd :INT:=0;
cStepInit :INT:=5;
cStepGetItem :INT:=10;
cStepGetItemReset :INT:=20;
cStepGetItemError :INT:=990;
cStepGetJoints :INT:=30;
cStepGetJointsReset :INT:=40;
cStepGetJointsError :INT:=991;
cStepGetJointsStr :INT:=50;
cStepGetJointsStrReset:INT:=60;
cStepGetJointsStrError:INT:=992;
cStepSetJointStrDelay :INT:=69;
cStepSetJointsStr :INT:=70;
cStepSetJointsStrReset:INT:=80;
cStepSetJointsStrError:INT:=993;
cStepEnd :INT:=300;
cStepWaitReset :INT:=999;
END_VAR
VAR
aSplit :ARRAY[1..11] OF STRING(80);
bResultSplit :BOOL;
debug:BOOL;
URL :STRING:='http://192.168.3.42:8091';
END_VAR
bConnected:=OPCUA_VirtualClient_RoboDK_Station.bConnected;
CASE iStep OF
cStepWaitCmd:
IF bStart THEN
iStep:=cStepInit;
bStart:=FALSE;
END_IF
cStepInit:
StationPointer:=0;
FOR i :=1 TO 11 DO
arrJoints[i]:=0.0;
arrJointsFromStr[i]:=0.0;
aSplit[i]:='';
END_FOR
IF NOT OPCUA_VirtualClient_RoboDK_Station.getItem.bBusy
AND NOT OPCUA_VirtualClient_RoboDK_Station.getItem.bError
AND NOT OPCUA_VirtualClient_RoboDK_Station.getJoints.bBusy
AND NOT OPCUA_VirtualClient_RoboDK_Station.getJoints.bError
AND NOT OPCUA_VirtualClient_RoboDK_Station.getJointsStr.bBusy
AND NOT OPCUA_VirtualClient_RoboDK_Station.getJointsStr.bError
AND NOT OPCUA_VirtualClient_RoboDK_Station.setJoints.bBusy
AND NOT OPCUA_VirtualClient_RoboDK_Station.setJoints.bError
AND NOT OPCUA_VirtualClient_RoboDK_Station.setJointsStr.bBusy
AND NOT OPCUA_VirtualClient_RoboDK_Station.setJointsStr.bError
THEN
iStep:=cStepGetItem;
END_IF
iStep:=cStepGetItem;
cStepGetItem:
IF OPCUA_VirtualClient_RoboDK_Station.getItem.bDone THEN
iStep:=cStepGetItemReset;
Item_ID:=OPCUA_VirtualClient_RoboDK_Station.getItem.Item_ID;
ELSIF OPCUA_VirtualClient_RoboDK_Station.getItem.bError THEN
iStep:=cStepGetItemError;
END_IF
cStepGetItemReset:
IF NOT OPCUA_VirtualClient_RoboDK_Station.getItem.bError
AND NOT OPCUA_VirtualClient_RoboDK_Station.getItem.bBusy
THEN
iStep:=cStepGetJoints;
END_IF
cStepGetJoints:
IF OPCUA_VirtualClient_RoboDK_Station.getJoints.bDone
AND NOT OPCUA_VirtualClient_RoboDK_Station.getJoints.bBusy
THEN
iStep:=cStepGetJointsReset;
ELSIF OPCUA_VirtualClient_RoboDK_Station.getJoints.bError THEN
iStep:=991;
END_IF
cStepGetJointsReset:
IF NOT OPCUA_VirtualClient_RoboDK_Station.getItem.bError
AND NOT OPCUA_VirtualClient_RoboDK_Station.getItem.bBusy
THEN
iStep:=cStepGetJointsStr;
END_IF;
cStepGetJointsStr:
IF OPCUA_VirtualClient_RoboDK_Station.getJointsStr.bDone
AND NOT OPCUA_VirtualClient_RoboDK_Station.getJointsStr.bBusy
THEN
iStep:=cStepGetJointsStrReset;
ELSIF OPCUA_VirtualClient_RoboDK_Station.getJointsStr.bError THEN
iStep:=cStepGetJointsStrError;
END_IF
cStepGetJointsStrReset:
IF NOT OPCUA_VirtualClient_RoboDK_Station.getJointsStr.bError
AND NOT OPCUA_VirtualClient_RoboDK_Station.getJointsStr.bBusy
THEN
iStep:=cStepSetJointStrDelay;
END_IF;
cStepSetJointStrDelay:
strJointsCommand:=''; strJointsCommand:=CONCAT(LREAL_TO_STRING(arrJointsCommand[1]),strJointsCommand);
strJointsCommand:=CONCAT(strJointsCommand,',');
strJointsCommand:=CONCAT(strJointsCommand,LREAL_TO_STRING(arrJointsCommand[2]));
strJointsCommand:=CONCAT(strJointsCommand,',');
strJointsCommand:=CONCAT(strJointsCommand,LREAL_TO_STRING(arrJointsCommand[3]));
strJointsCommand:=CONCAT(strJointsCommand,',');
strJointsCommand:=CONCAT(strJointsCommand,LREAL_TO_STRING(arrJointsCommand[4]));
strJointsCommand:=CONCAT(strJointsCommand,',');
strJointsCommand:=CONCAT(strJointsCommand,LREAL_TO_STRING(arrJointsCommand[5]));
strJointsCommand:=CONCAT(strJointsCommand,',');
strJointsCommand:=CONCAT(strJointsCommand,LREAL_TO_STRING(arrJointsCommand[6]));
TON2(IN:=TRUE,PT:=T#0.2S);
IF TON2.Q THEN
TON2(IN:=FALSE);
iStep:=cStepSetJointsStr;
END_IF
cStepSetJointsStr:
IF (
OPCUA_VirtualClient_RoboDK_Station.setJointsStr.bDone
AND NOT
OPCUA_VirtualClient_RoboDK_Station.setJointsStr.bBusy
)
OR NOT bWrite
THEN
iStep:=cStepSetJointsStrReset;
ELSIF OPCUA_VirtualClient_RoboDK_Station.setJointsStr.bError
THEN
iStep:=cStepSetJointsStrError;
END_IF
cStepSetJointsStrReset:
bWrite:=FALSE;
OPCUA_VirtualClient_RoboDK_Station.setJointsStr.bExecute:=FALSE;
IF NOT OPCUA_VirtualClient_RoboDK_Station.setJointsStr.bError
AND NOT OPCUA_VirtualClient_RoboDK_Station.setJointsStr.bBusy
THEN
iStep:=cStepEnd;
END_IF;
cStepEnd:
TON(IN:=TRUE,PT:=T#0.1S);
IF TON.Q THEN
TON(IN:=FALSE);
IF NOT debug THEN
iStep:=10;
ELSE
iStep:=cStepSetJointStrDelay;
END_IF;
END_IF
cStepGetItemError:
Item_ID:=0;
iStep:=cStepWaitReset;
cStepGetJointsError:
FOR i :=0 TO 11 DO
arrJoints[i]:=-99999.99;
END_FOR
iStep:=cStepWaitReset;
cStepGetJointsStrError:
strJoints:='';
iStep:=cStepWaitReset;
cStepWaitReset:
IF bReset THEN
iStep:=cStepInit;
bReset:=FALSE;
END_IF;
END_CASE
aSplit[1] := strJoints;
FOR i:=1 TO 7 DO
bResultSplit := FindAndSplit(
pSeparator := ADR(sSeparator)
,pSrcString := ADR(aSplit[i])
,pLeftString:= ADR(aSplit[i])
,nLeftSize := SIZEOF(aSplit[i])
,pRightString:= ADR(aSplit[i+1])
,nRightSize := SIZEOF(aSplit[i+1])
,bSearchFromRight := FALSE );
IF NOT bResultSplit THEN
EXIT;
END_IF
END_FOR
FOR i :=1 TO 6 DO
arrJointsFromStr[i]:=STRING_TO_LREAL(aSplit[i]);
END_FOR;
//
OPCUA_VirtualClient_RoboDK_Station.getItem(
bExecute:=iStep=cStepGetItem
,Item_Name:=Robot_name
);
OPCUA_VirtualClient_RoboDK_Station.getJoints(
bExecute:=iStep=cStepGetJoints
,Item_ID:=Item_ID,Joints=>arrJoints
);
OPCUA_VirtualClient_RoboDK_Station.getJointsStr(
bExecute:=iStep=cStepGetJointsStr
,Robot_name:=Robot_name,Joints=>strJoints
);
IF bWrite THEN
OPCUA_VirtualClient_RoboDK_Station.setJointsStr(
bExecute:=TRUE
,Robot_name:=Robot_name,Joints:=strJointsCommand);
END_IF;
This example will show you how you can add OPC-UA Client connectivity to RoboDK. RoboDK includes an OPC-UA add-in that allows you to add OPC UA compatibility to your RoboDK projects.
In this example you’ll learn how to get the data from the RoboDK Station via OPC UA Client.
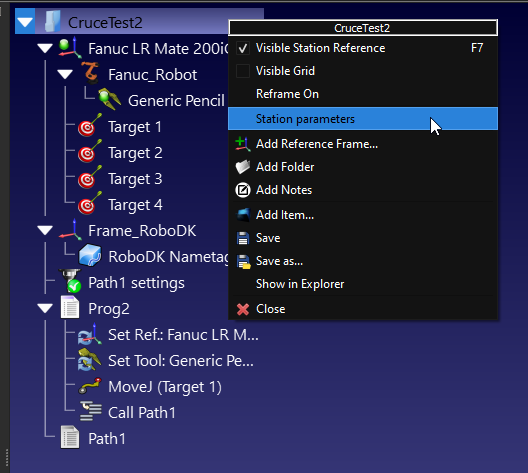
Station parameters screen is displayed and press “Clear All” to delete all Station parameters.
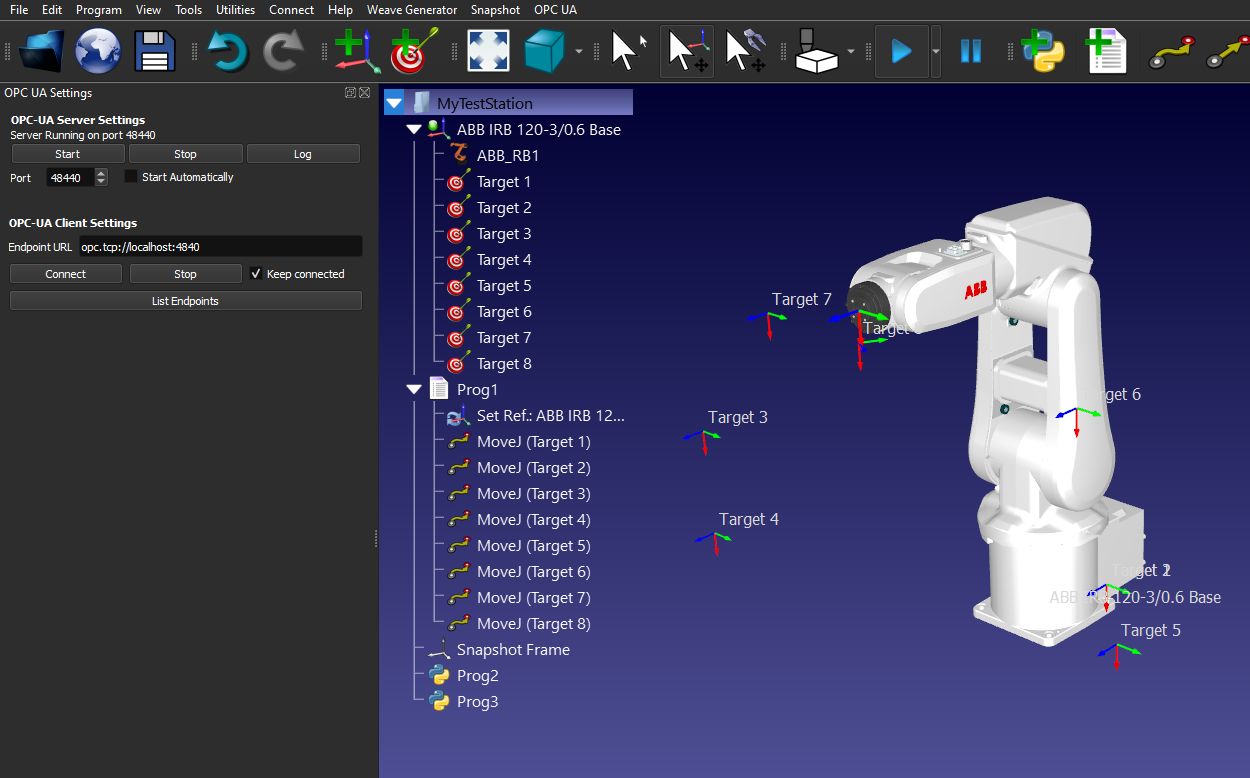
We can create one more RoboDK project with the OPC UA server is configurated and started.
This section shows how to add an OPC UA client.
Enter the Endpoint URL, for example: opc.tcp://127.0.0.1:48441.
You need to match the IP address and port configuration to your Target OPC UA server.
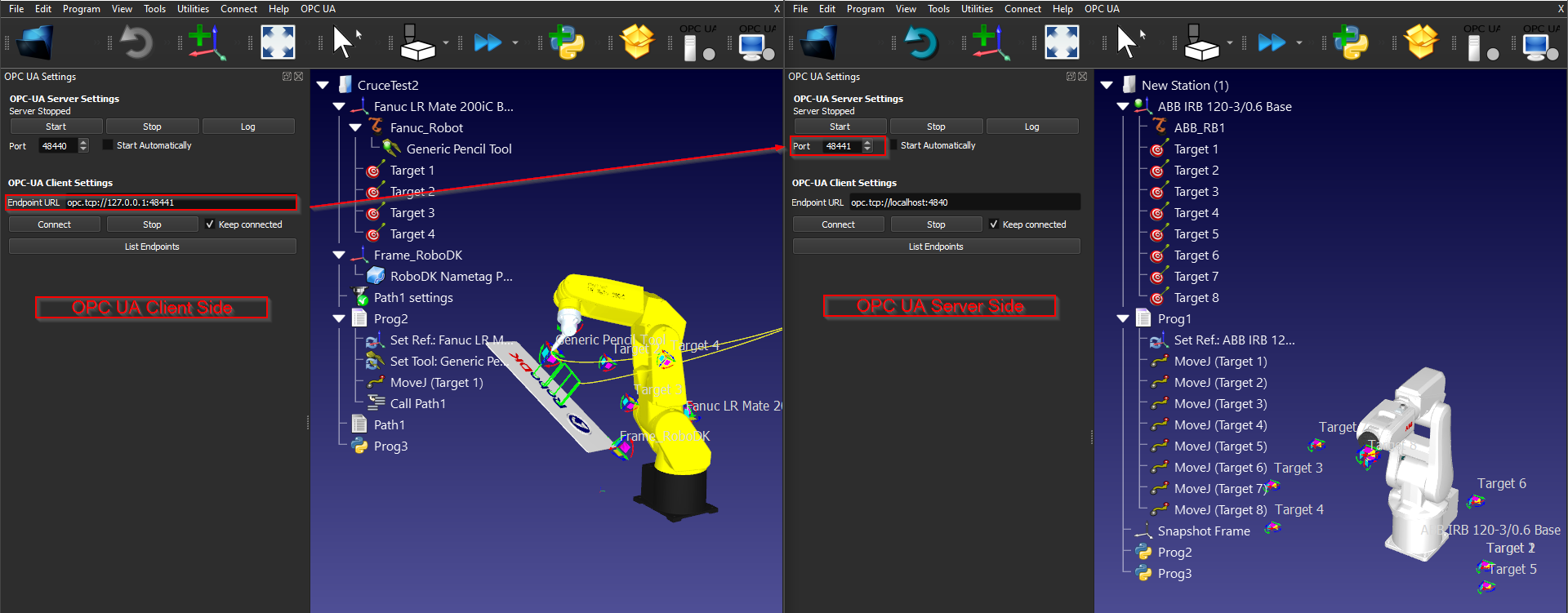
Press “Connect” to establish the connection.
如果有消息“retri服务器变量eved. Right Click the station item and select ‘Station parameters’ to see the variables.”, the connection is established.
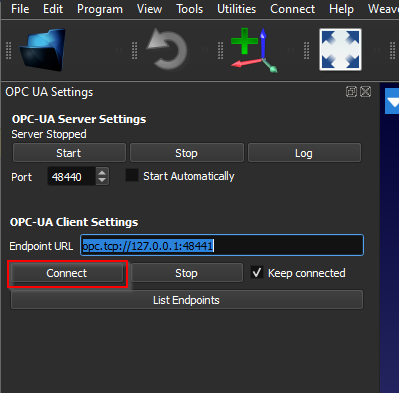
Right Click your Station and select “Station parameters”.
You can check the details of each Node from thenodessection.
After you get the Nodes data from OPC UA Server via OPC UA client in RoboDK, you can also get these data by using RoboDK-Python-API.
You can reference this link to install the RoboDK Python-API.
//www.sinclairbody.com/doc/en/PythonAPI/intro.html#how-to-install
Or install the robodk package for Python manually:
pip install robodk
This example script shows how to get the station parameters via the Python API of RoboDK.
from robodk import robolink # RoboDK API
RDK = robolink.Robolink()
from robodk import * # RoboDK API
from robolink import * # Robot toolbox
itemlist = RDK.ItemList()
if itemlist:
# Get all Station Parameters
print('Vaild Paramaters are configurated in your Station..')
StationParameters=RDK.getParams()
for StationParameter in StationParameters:
print("Station Parameters %s : %s"%(StationParameter[0],str((StationParameter[1]))))
else:
print('No Parameter list..')
Here is the result of the Example Script:
Vaild Paramaters are configurated in your Station..
站参数RoboDK: RoboDK 64位v5.5.3.23031
Station Parameters time : 02/14/2023 03:58:29.191.000.000
Station Parameters SimulationSpeed : 13.8551
Station Parameters Station : MyTestStation